PDCP:packet data convergence protocol (TS 38.323)
5G NR PDCP has 3 main functions:
1. Header Compression
2. Encryption
3. Reordering
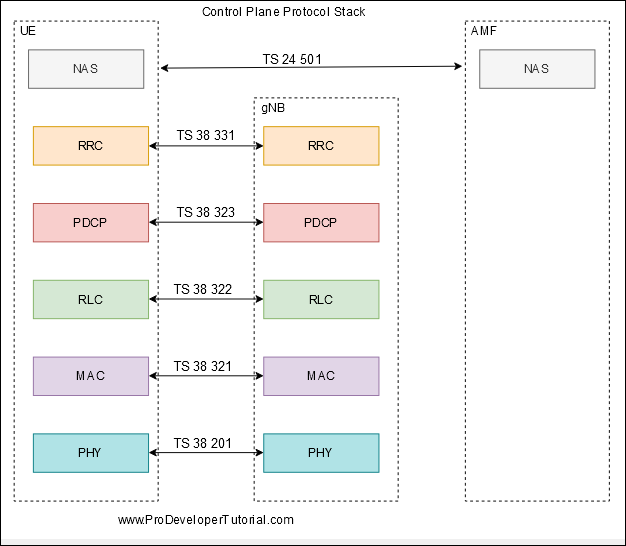
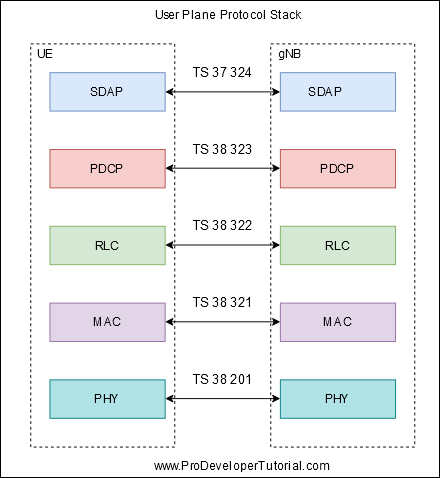
The PDCP sublayer is configured by upper layers TS 38.331 [3]. The PDCP sublayer is used for RBs mapped on DCCH and DTCH type of logical channels. The PDCP sublayer is not used for any other type of logical channels.
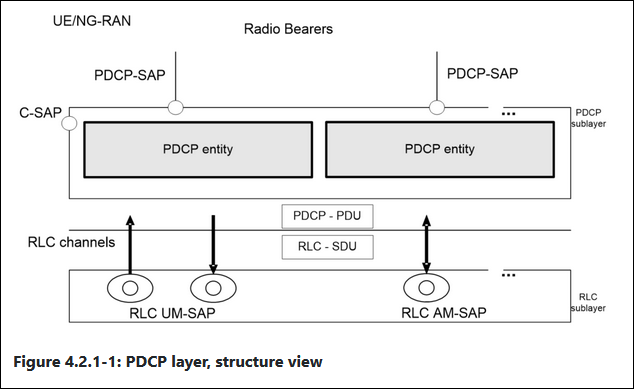
Each RB (except for SRB0) is associated with one PDCP entity.
Each PDCP entity is associated with one, two, or four RLC entities depending on the RB characteristic (e.g uni-directional/bi-directional or split/non-split) or RLC mode.
PDCP layer, structure view
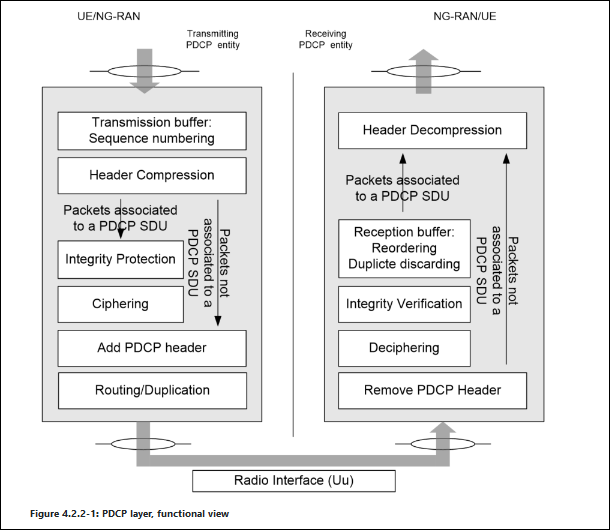
PDCP layer, functional view
——————————
PDCP will perform encryption function on the Data part which will not include SDPA header.
Data PDU carring SRB must be integrity protected and Data PDU carrying DRB can be integrity protected according to the configuration requirements.
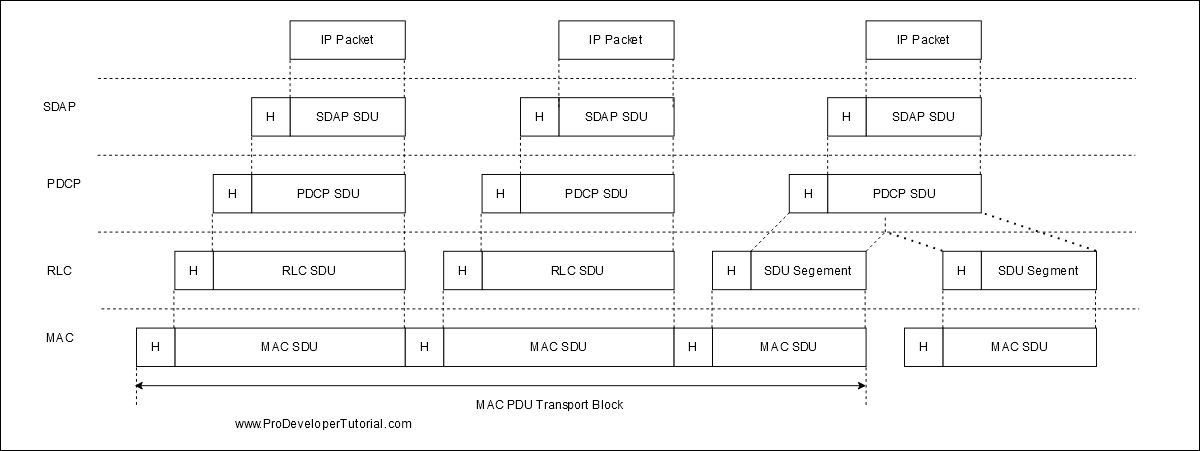
If a RB is segmented then routing and duplication functions are added.
Services provided to upper layers
he PDCP layer provides its services to the RRC or SDAP layers. The following services are provided by PDCP to upper layers:
– transfer of user plane data;
– transfer of control plane data;
– header compression;
– ciphering;
– integrity protection.
Services expected from lower layers
A PDCP entity expects the following services from lower layers per RLC entity:
– acknowledged data transfer service, including indication of successful delivery of PDCP PDUs;
– unacknowledged data transfer service.
The PDCP layer supports the following functions:
– transfer of data (user plane or control plane);
– maintenance of PDCP SNs;
– header compression and decompression using the ROHC protocol;
– ciphering and deciphering;
– integrity protection and integrity verification;
– timer based SDU discard;
– for split bearers, routing;
– duplication;
– reordering and in-order delivery;
– out-of-order delivery;
– duplicate discarding.
Source TS 38 323