In this chapter we shall learn about:
3.1 Introduction of Tree Traversal
3.2 Types of tree traversal
3.3 Breadth first traversal.
3.4 Depth first traversal.
3.5 Pre Order Traversal: DLR
3.6 In Order Traversal: LDR
3.7 Post Order Traversal: LRD
3.1 Introduction of Tree Traversal
A tree traversal can be defined as the process of visiting each node exactly once in some order.
As we know that trees are non linear data structure, we start from root node. Then we have 2 possible directions, i.e to go left or to go right.
3.2 So tree traversal can be done in 2 ways:
1. Breadth first traversal.
2. Depth first traversal.
This type of traversal holds good for both trees and graphs. [We shall discuss graph in next chapter]. In this chapter we shall learn related to trees.
3.3 Breadth first traversal.
In Breadth first traversal, we shall visit all the nodes at the same level before visiting the nodes at the next level.
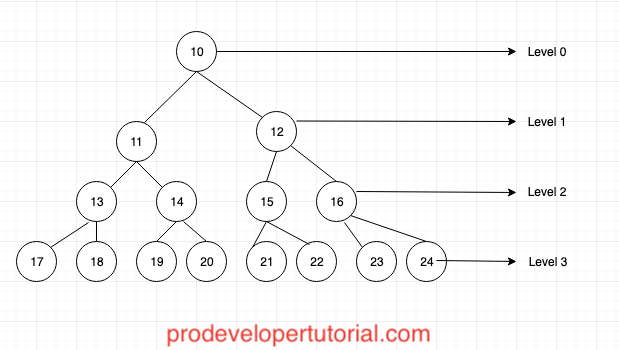
In Breadth First approach, we should start from Level 0, then cover all the nodes in that level, then go to the next level.
So first we visit the root node at level 0. The root node value is “10”. Then we go to level 1, and then visit the nodes from left to right. Then nodes at level 1 are “11” “12”.
Now we completed level 1, then visit level 2. The nodes at level 2 are “13” “14” “15” “16”.
Now we visit level 3. The nodes at level 3 are “17” “18” “19” “20” “21” “22” “23” “24”.
When we combine all the nodes from all the level we get:
“10” “11” “12” “13” “14” “15” “16” “17” “18” “19” “20” “21” “22” “23” “24”.
This traversal is also called as level order traversal.
3.4.Depth first traversal.
In this approach, once we get a child, we would complete the whole sub tree of that child before going to the next child.
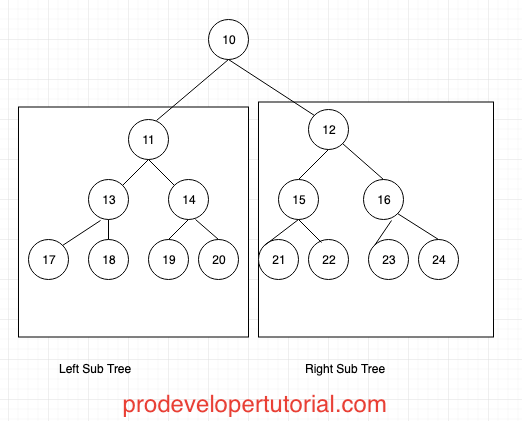
In our example, “10” is the root node. If we select “11” child, then we need to complete all the nodes present in that “11” sub tree. Then we should go to Right Sub Tree. Like wise we traverse all the nodes in the tree.
To do Depth First Traversal, we have multiple options as shown below:
root -> left child -> right child.
root -> right child -> left child.
left child -> root -> right child.
Depending on how we traverse we have 3 options.
1. Pre Order Traversal i.e root -> left -> right
2. In Order Traversal i.e left -> root -> right
3. Post Order Traversal i.e left -> right -> root
In total we have 6 possible permutations. But above 3 are the commonly used strategies.
To remember the traversal easily, if we consider root as “D” as in data, left as “L” and right as “R” we get:
Pre Order Traversal: DLR
In Order Traversal: LDR
Post Order Traversal: LRD
Now let us understand how the above 3 traversals are done.
We shall consider the below image as an example.
3.5 Pre Order Traversal: DLR
In this type of traversal, we visit the root node first, then visit left node, then right node.
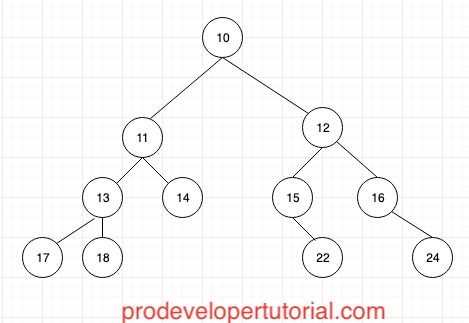
First visit the root node “10”, then go to left sub tree “11”, then again “13” has a child “17”, visit it.
Hence we have visited all the nodes to the left.
“10” “11” “13” “17”.
There are no left sub tree to visit. Hence go one level up i.e “13”. “13” node, left sub tree is completed. But we did not complete right sub tree. Hence visit it i.e “18”.
“10” “11” “13” “17” “18”.
Now we have completed node “13”. Go one level up to “11”. As we have visited left sub tree, go to right sub tree i.e “14”.
“10” “11” “13” “17” “18” “14”.
Now we have completed the left sub tree of root node. Now we go to right sub tree of root node.
Now we go to “12” node. Node “12” has a left node “15” visit it. Then Node “15” does not have left sub tree, but has a right sub tree visit it i.e “22”.
“12” “15” “22”
Now that we have complete node “15” go one level up to node “12”. Visit all the nodes at right sub tree. i.e “16” “24”.
Hence the total order of visiting of all the nodes in pre order traversal is
“10” “11” “13” “17” “18” “14” “12” “15” “22” “16” “24”
3.6 In Order Traversal: LDR
In this traversal we visit left sub tree, then root then right sub tree.
In our example, we start with root node “10”, traverse to left i.e “11”, then “13”, then “17”. As “17” node doesn’t have any left sub tree, start with that, then visit it’s root i.e “13”, then to its right, i.e “18”.
Hence we get
“17” “13” “18”.
Then go one level up, to node “11”, as we have visited left sub tree, go to right i.e “14”.
“17” “13” “18” “11” “14”.
Then go to root node “10”.
“17” “13” “18” “11” “14” “10”.
Then go to right sub tree “12”, in that go to left sub tree “15”, as “15” does not have left sub tree, visit right sub tree “22”
Hence we get “15”, “22”
Go one level up “12”, then visit right sub tree “16” “24”
Total of right sub tree will be
“15”, “22”, “12”, “16” “24”.
Total In order traversal will be:
“17” “13” “18” “11” “14” “10” “15”, “22”, “12”, “16” “24”.
3.7 Post Order Traversal: LRD
In post order traversal, we visit the left sub tree first, then right sub tree, then to the root node.
In our example, we first go to 10 -> 11 -> 13 -> 17.
First we visit 17 node, then 18, then 13.
“17”, “18”, “13”.
Then we go one level up to node “11”, visit node “14”, then visit “11”.
Hence the left sub tree will be
“17”, “18”, “13”, “14”, “11”.
Note: Now we don’t visit the root node, we need to go to right sub tree.
Now traverse 12 -> 15 -> 22
Now visit the node “22”, then “15”,
“22”, “15”
Then go one level up to node 12. Traverse 16 -> 24.
Visit “24”, “16” then “12” then “10”.
Right sub tree will be
“22”, “15”, “24”, “16”, “12”, “10”
Total traversal will be:
“17”, “18”, “13”, “14”, “11” ,“22”, “15”, “24”, “16”, “12”, “10”
Further Reading: