In this chapter we shall learn system design for online file sharing services like Dropbox or google drive.
Below is the list of features that we shall be discussing:
- Upload and download
- Sync data
- History of file changes
Assumptions on the number of requests that the server will be receiving:
10Million users
100Million requests/day
High read and write
Designing a file sharing service is not as simple as uploading a document and whenever the file changes, upload the file again. This is not going to work.
Consider the following scenario:
If the user has a very long file like 20MB and every time the user makes a changes, you will be uploading whole file, if he makes just small changes like adding a space or changing a spelling mistake for 5 times, then it will be 100MB bandwidth. That is not efficient.
So instead of uploading the whole file, what we can do is to break the file into smaler parts of 2MB each. Thus making 10 parts or chunks. So for the first time, we upload all the files to the cloud. Then the user makes a changes, then we upload only the chunk where the file has been updated. Thus saving bandwidth and the latency. For this you can use HDFS to serve thsi purpose.
So now let us talk about how to design the service.
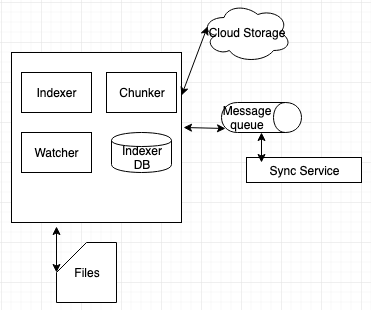
From the above image we have a client that is installed in mobile device or on a laptop. Below is the basic list of components the client should have to provide basic file sharing functionality:
4.1. Watchman:
Initially when we setup a client, we configure a folder to the client. The watchman will be watching this folder. When there is a change in the folder, it will automatically notifies the Divider and Indexer.
4.2. Divider/Chunker:
Once the divider gets a notification from the watchman, that a new file has been added, it will divide the data into chunks and uploads to the cloud. You can use AmazonS3.
4.3. Indexer:
Once the divider divides the file, it will take a hash value of the data. Then divider service uploads the data to the cloud, it will get the URL where it is stored in the cloud. The hash of the data along with the URL will be maintained by the indexer.
4.4. DB indexer:
It will save the data that has been received from indexer.
Then we have a messaging service that will have the queue of the data that has been changed. This is needed because, there might be multiple clients, if one client changes the data, that data should be replicated in all the clients. The messaging service will broadcast the updated data to all the clients connected. Now the clients will learn that there has been a file change, they will look into the indexer and compare if all the data are same or different. If the data is different, then it will updated the data. You can use RabbitMQ or kafka for message queue.
4.5 Metadata:
We need a metadata to store the information like file history, message chunk hash and its uploaded URL, the clients connected to the service. As we need the data to be consistent, we need to use RDBMS as there will be many clients connected. If you use NoSQL it will provide eventual consistency.
This is the basic system design for file upload service.