HARQ stands for Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (HARQ).
This is a physical layer functionality in LTE.
It is type of error detection and correction technique.
It uses forward error correction.
ARQ: Automatic Repeat Request.
It means, if the sender doesn’t receive ACK from the receiver before timeout, then the receiver will discard the packet and sender will retransmit the packet.
For example:
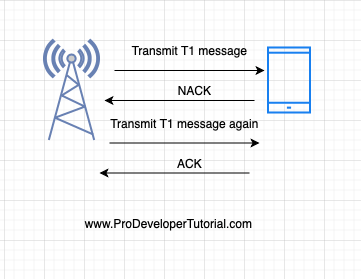
The eNB is sending T1 block to the smart-phone, but the smart phone has received half of the data. Hence it will send a NACK. Again the sender will send the same T1 block again.
This is not an efficient way to handle the error.
HARQ
Maximum 3 times HARQ NACK can be sent.
Soft Combining:
Soft Combining one method to correct the errors. Errors might be due to the bad packets, that might have lost during the transmission.
In soft combining, the bad block will not be discarded, but will be kept, and bad packets will be taken from the next re-transmitted block. This is called as HARQ.
Incremental Redundancy with Soft Combining
This type of HARQ is used in LTE.
This is across 2 layers, between MAC and Physical Layer.
MAC layer will do Incremental Redundancy
Physical Layer will do the Soft Combining
Incremental Redundancy: It is change the coding from transmitted from re-transmitted.
It will have maximum of 8 level. After that, it will drop the packet fully.
Hence HARQ retransmissions are faster than compared to RLC based retransmission.
There are 2 level of re-transmission for error correction.
HARQ at MAC layer
ARQ at RLC layer.
ARQ will try to handle errors that are not corrected by HARQ.
Different types of HARQ :
There are 2 different types of HARQ:
- Synchronous HARQ, used for uplink
- Asynchronous HARQ, used for downlink.
Synchronous and Asynchronous HARQ:
In Synchronous HARQ, retransmission is known at what time it will occur. Hence this will not require the packet number for retransmission. It can operate in minimum signaling overhead.
In asynchronous HARQ, retransmission processes can occur at any time. Hence, explicit signaling like HARQ process number is required to transmit each retransmission packets. This will require a signaling overhead.
Different types of Synchronous HARQ: Adaptive or Non-Adaptive:
In adaptive HARQ, transmission parameters like code rate, number of resource allocation, and modulation order may change during retransmissions.
In non-adaptive HARQ, retransmission packet format is not changed or know to both communicating parties.
Quantity of HARQ process is required for a packet:
There are 8 HARQ process required for a single packet and there is 8ms round trip time.
Calculation:
Tx packet transmission : 1 ms
Rx received and processed: 3 ms
RX NACK transmit time :1 ms
Tx process NACK & retransmission time : 3 ms
Overall Time consuming : 8 ms
Need of HARQ instead of RLC ARQ?
As RLC will be having multiple instances of Rx and Tx that will be dealing with multiple logical channels CCCH, DCCH, DTCH., there will be waste of system resources.
Hence when MAC layer multiplex all the packets from multiple RLC entities and send it to the PHY, HARQ correction will be after and efficient.
HARQ Mechanisms
HARQ Type1:
If the channel quality is good, it will receive all the packets correctly. It will rectify all the transmission information.
If the channel quality is bad, and if not all the transmission errors can be corrected, then that packet will be discarded. And an request for retransmission will be requested.
HARQ Type2:
FEC and ED (Error Detecting) will be known to decrypt the data block correctly.
Notes:
In FDD, ACK/NACK refers to the downlink packet.
In TDD, ACK/NACK timing depends on the uplink/downlink configuration.
UE can request retransmission of data packets that were incorrectly received on PDSCH
8 HARQ process can be used.
Click here for complete 4G/LTE tutorials for free