In the previous chapter we have solved fractional knapsack problem. In this chapter we shall solve 0/1 knapsack problem.
Problem Statement:
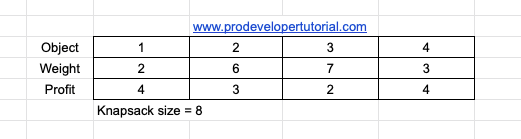
You are given ‘n’ number of object with their weights and profits.
You are given a bag with max capacity it can hold. Objective here is to fill the bag/knapsack so that you get max profit.
As this is 0/1 knapsack problem, you can either take the whole object or don’t take the object at all.
We can solve this problem with help of Dynamic Programming. We cannot solve it with help of greedy approach.
Before we solve using DP, we shall see how to solve it with help of brute force approach.
In brute force approach, we take an array of size ‘n’, then mark the objects as 1, if we select it.
For example:
We have 4 objects and hence we take an array of size 4 and initialize it to 0.
[0, 0, 0, 0]
If we user the object 1 and 4, we make them as 1 and calculate the profit.
[1, 0, 0, 1] the total weight will be 2 + 3 = 5 and profit will be 4 + 4 =8.
Similarly, we do all the combinations and check the profit whose weight is less than or equal to 8. Then select the max profit.
This will take 2^n time and is not optimal.
Hence we shall use Dynamic Programming to solve the problem.
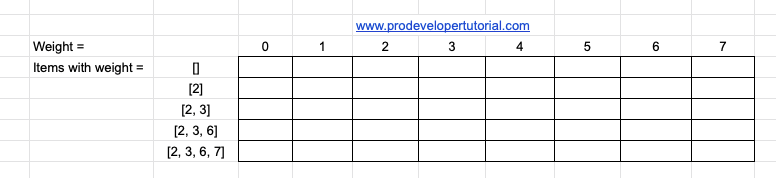
As always in DP, we first write our DP table:
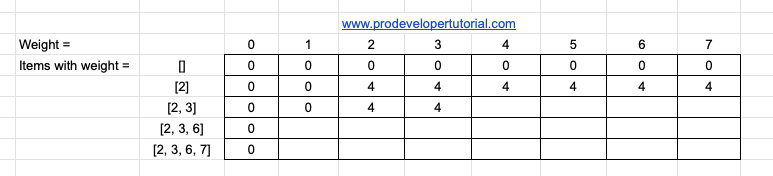
In the above table, we can see that, in the row we have taken individual weights. In the column, we have taken the weights of item in increasing order [ascending].
In the DP table we fill with the profit value for the selected item.
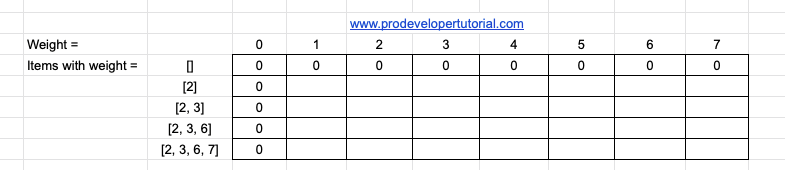
So, when the total weight is 0, the profit will also be 0. SO we shall fill our table as below:
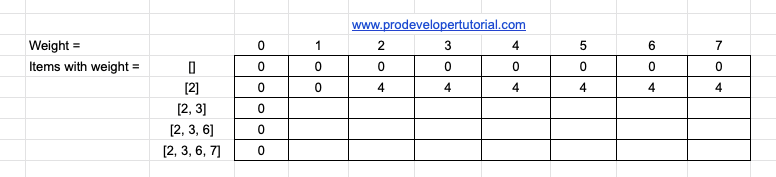
Now, we have chosen an item with weight 2. So till weight 2, the profit will be 0. And after weight 2, the profit will be ‘4’. Because ‘4’ is the profit for 2.
As we have only 1 item with weight 2, the profit for all the items will be 4.
The updated DP table is as below:
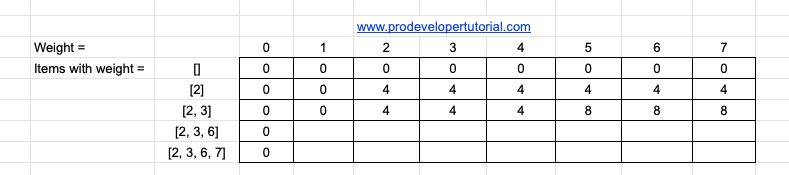
Now we have weights [2, 3]. So till weight 2, we copy the values from above table.
Now when we arrive at weight 3, we have 2 choices. Either choose weight 2 with profit 4 or weight 3 with profit 4. As both of the profits are same, we can either choose object with weight 2 or object with weight 3.
Now at weight 4, the profit will remain the same
But at weight 5, we can choose both objects with weight 2 and object with weight 3. So the total profit will be 8. It will be continued till weight 7.
From the above table, can we make out a formula to fill the values in the table?
Yes, below is the formula:
max [ [i-1, j], [value_at_i + [i-1, j-weight] ] ]
Implementation of 0/1 knapsack problem using C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
int knapSack(int knapsack_size, int weight[], int object[], int n)
{
int i, w;
int DP[n + 1][knapsack_size + 1];
for(i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for(w = 0; w <= knapsack_size; w++)
{
if(i == 0 || w == 0)
DP[i][w] = 0;
else if(weight[i - 1] <= w)
DP[i][w] = max(object[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][w - weight[i - 1]], DP[i - 1][w]);
else
DP[i][w] = DP[i - 1][w];
}
}
return DP[n][knapsack_size];
}
int main()
{
int object[] = {2, 6, 7, 3};
int weight[] = {4, 3, 2, 4};
int knapsack_size = 8;
int n = sizeof(weight) / sizeof(weight[0]);
cout << "The solution for knapsack 0/1 is = "<< knapSack(knapsack_size, weight, object, n)<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
The solution for knapsack 0/1 is = 13
Further Reading: