Introduction:
There are 2 variants of Knapsack Problem
- General Knapsack problem / Fractional Knapsack problem: Here the items can be divided. This problem can be solved by greedy method.
- 0/1 knapsack problem: Where the items cannot be divided. Either you take the whole item[1] or dint take the item [0]. Hence 0/1. This can be solved by dynamic programming approach.
In this tutorial we shall look at first type of knapsack problem with greedy approach.
This problem is also called as Fractional Knapsack problem. Because we are allowed to divide the items to get maximum profit.
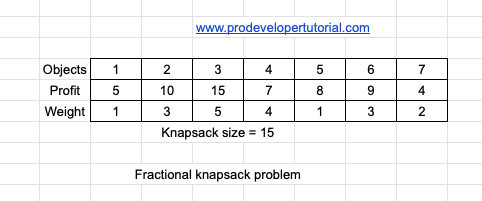
Problem Statement: You are given with ‘n’ objects with their weights and profit. You are also given a bag or knapsack of certain size.
Your objective is to fill that knapsack with maximum profit.
Consider the input below:
According to the objective, you need to fill the knapsack with the weight of 15 or less with maximum profit.
We shall solve this problem with help of greedy approach.
Note: This problem can also be solved with the help of Dynamic Programming. But in this tutorial we shall learn about greedy approach only.
To solve this problem with the help of greedy approach, it can be solved in 3 different ways.
1stMethod: Select the item with maximum profit and fill the bag till weight is 15.
In our example, 1stmax profit it 15, and weight is 5.
Then, 2ndmax profit it 10, and weight is 3.
Then, 3rdmax profit it 9, and weight is 3.
Accordingly, we can solve the problem.
2ndMethod:
Select the items with minimum weight, so that we can choose more items there by increasing the profit.
3rdMethod:
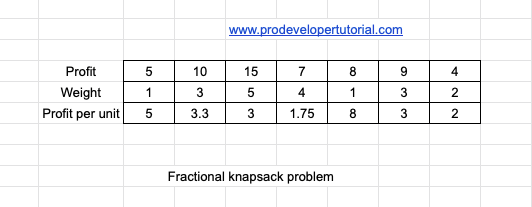
In this method we divide profit with weight, there by giving us the profit for 1 unit.
For example, for the item ‘3’, the profit is 15 and weight is 5. Now we calculate the profit for 1kg. We can do it by 15/5 =3.
Hence for 1 kg we get ‘3’ profit.
Like this we calculate the profit per unit for all the items. Then we select the items based on it.
We shall use this method to solve the fractional Knapsack problem.
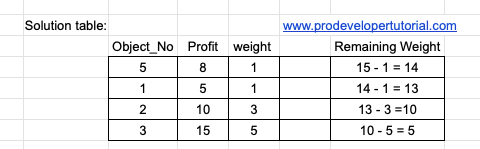
The new table will be as below:
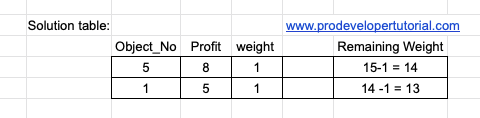
Now let’s select the items, where we get max profit for min weight.
Note: While choosing the max profit for min weight, you need to keep in mind about the total weight present for a particular object. For example, for 5thobject, it has weight “1” and profit “8”, it can be used only once because the weight is 1.
As the weight of object is 5 is 1, we have used it. Hence we are done with this object. Next height profit is 5, we get:
Now we are done with object 1, as weight is 1. Next we have “3.3” with max profit. Hence we get:
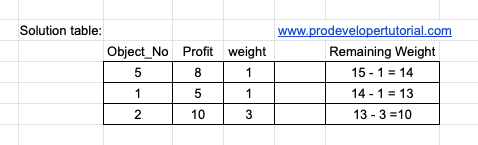
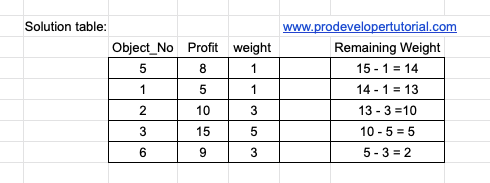
Next we have “3”. For profit “3” we have object 3 and object 6. We select object 3 we get:
Next we select object 6.
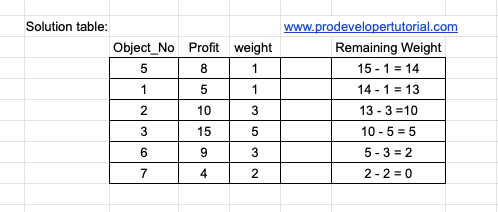
Next we select object 7.
Hence total profit is 51. This is our answer.
Implementation of Fractional knapsack using C++
#include <utility>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
//first is profit second is weight
typedef std::pair<double, double> item;
//return if first item has greater value by weight ratio than the
bool comp_item(item& a, item& b)
{
return a.first/a.second > b.first/b.second;
}
double fractional_knapsack(item items[], int n, double capacity)
{
double profit= 0;
//sort items by their value/weight ratio in decreasing order
sort(items, items+n, comp_item);
for(int i= 0; i<n; i++)
{
if(items[i].second <= capacity)
{
capacity -= items[i].second;
profit += items[i].first;
}
else
{
profit += items[i].first/items[i].second * capacity;
capacity= 0;
break;
}
}
return profit;
}
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int n;
item items[100];
double capacity;
cout<<"Enter the number of items\n";
cin>>n;
cout<<"Enter the total capacity of knapsack\n";
cin>>capacity;
cout<<"Enter the profit and weight for "<< n <<" items\n";
for(int i= 0; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>items[i].first>>items[i].second;
}
cout<< "The maximum profit is = " fractional_knapsack(items, n, capacity) <<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter the number of items 7 Enter the total capacity of knapsack 15 Enter the profit and weight for 7 items 5 1 10 3 15 5 7 4 8 1 9 3 4 2 The maximum profit is = 51
Further Reading: