Below are different types of inheritance:
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
- Multipath Inheritance / Diamond Problem
- Accessibility in Inheritance
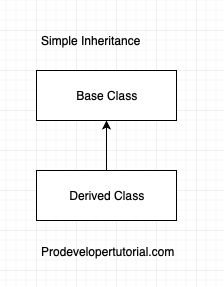
1. Single Inheritance
In this type of inheritance, there will be only 1 base class, and one derived class.
It can be visualized as below:
Program for Single Inheritance:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class BaseClass
{
public:
void display_base()
{
cout<<"Display from base class"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass: public BaseClass
{
public:
void display_derived()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
DerivedClass d;
d.display_derived();
}
Output:
Display from derived class
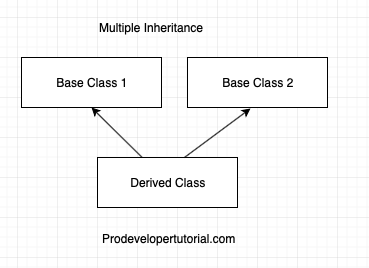
2. Multiple Inheritance
In multiple inheritance, once derived class and will be inheriting from multiple base class.
Below is the visualization of the same
Program from Multiple Inheritance
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_base_1()
{
cout<<"Display from base class 1"<<endl;
}
};
class BaseClass_2
{
public:
void display_base_2()
{
cout<<"Display from base class 2"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass: public BaseClass_1, public BaseClass_2
{
public:
void display_derived()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
DerivedClass d;
d.display_derived();
d.display_base_1();
d.display_base_2();
}
Output:
Display from derived class Display from base class 1 Display from base class 2
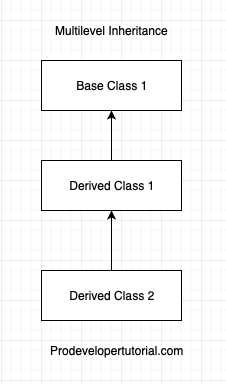
3. Multilevel Inheritance
In this type of inheritance, a derived class will be a base class for another class.
Representation for Multilevel Inheritance
Program for Multilevel Inheritance:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_base_1()
{
cout<<"Display from base class 1"<<endl;
}
};
class BaseClass_2: public BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_base_2()
{
cout<<"Display from base class 2"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass: public BaseClass_2
{
public:
void display_derived()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
DerivedClass d;
d.display_derived();
d.display_base_1();
d.display_base_2();
}
Output:
Display from derived class Display from base class 1 Display from base class 2
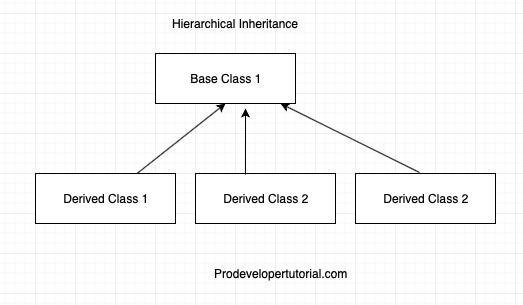
4. Hierarchical Inheritance
In this type of inheritance, one base class will be derived by many child class.
Representation of Hierarchical Inheritance
Program for Hierarchical Inheritance:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_base_1()
{
cout<<"Display from base class 1"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass_1: public BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_derived_1()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class 1"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass_2: public BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_derived_2()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class 2"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
DerivedClass_1 d1;
d1.display_derived_1();
DerivedClass_2 d2;
d2.display_derived_2();
}
Output:
Display from derived class 1 Display from derived class 2
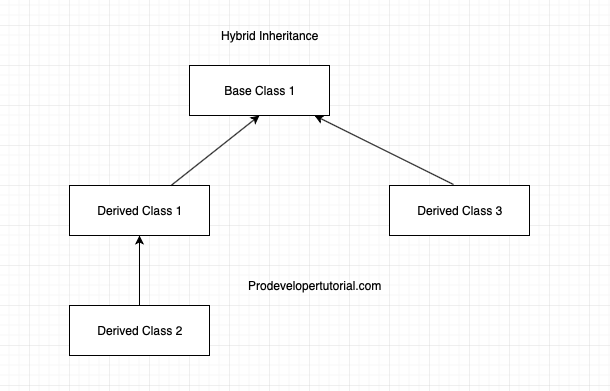
5. Hybrid Inheritance
In this type of inheritance is a mixture of above discussed inheritance types.
Representation of Hybrid Inheritance
Program for Hybrid Inheritance:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_base_1()
{
cout<<"Display from base class 1"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass_1: public BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_derived_1()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class 1"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass_2: public DerivedClass_1
{
public:
void display_derived_2()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class 2"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass_3: public BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_derived_3()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class 3"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
DerivedClass_1 d1;
d1.display_derived_1();
DerivedClass_2 d2;
d2.display_derived_2();
DerivedClass_3 d3;
d3.display_derived_3();
}
Output:
Display from derived class 1 Display from derived class 2 Display from derived class 3
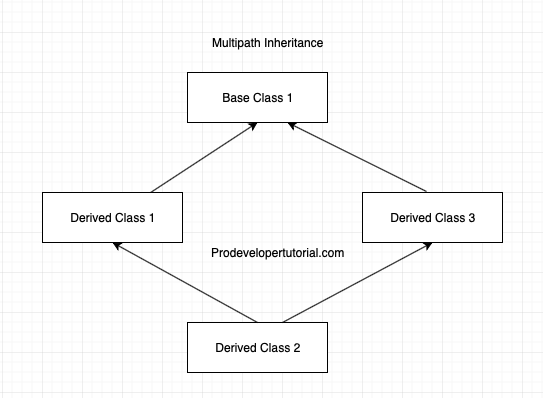
6. Multipath Inheritance / Diamond Problem
In this type of inheritance, there will be multiple path to a base class. Hence this will result in a derived class having multiple member of same base class members. This will result in error.
Image for Multipath Inheritance:
From the above image we can see that, “Derived Class 2” is inherited from “Derived Class 1” and “Derived Class 3”. Because of this “Derived Class 2” will have multiple copies of members from “Base class”. This type of inheritance is called as Multipath Inheritance.
This will lead to Diamond Problem. This can be solved by using Virtual Inheritance.
Example for Multipath Inheritance:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_base_1()
{
cout<<"Display from base class 1"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass_1: public BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_derived_1()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class 1"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass_3: public BaseClass_1
{
public:
void display_derived_3()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class 3"<<endl;
}
};
class DerivedClass_2: public DerivedClass_1, public DerivedClass_3
{
public:
void display_derived_2()
{
cout<<"Display from derived class 2"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
DerivedClass_1 d1;
d1.display_derived_1();
DerivedClass_2 d2;
d2.display_derived_2();
DerivedClass_3 d3;
d3.display_derived_3();
}
Output:
Display from derived class 1 Display from derived class 2 Display from derived class 3
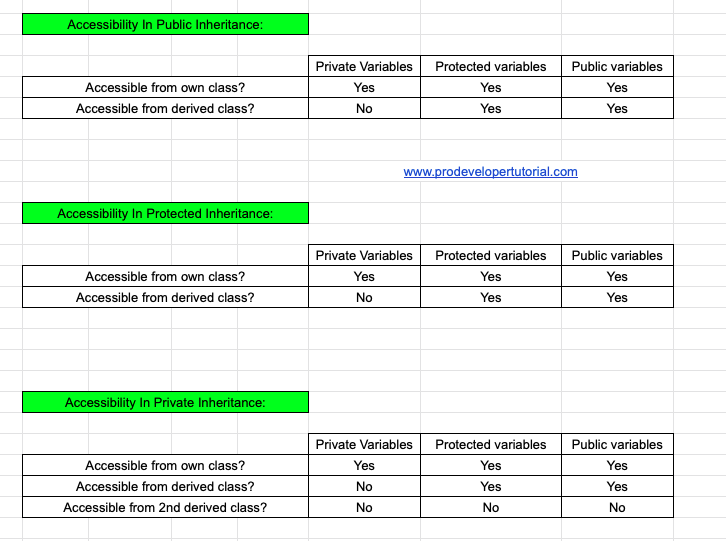
7. Accessibility in Inheritance
In the below table we shall see how the accessibility changes with different types of Inheritance.