What is a Stack?
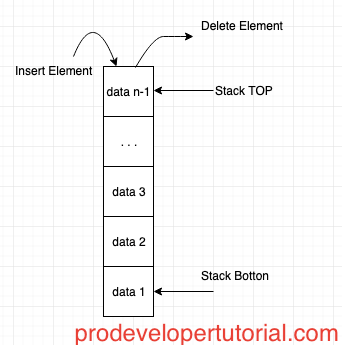
Stack is a special type of data structure where in the elements are entered from one end and are deleted from same end.
Stack is also called as Last In First Out data structure [LIFO]. Because the elements that are entered Last will be removed at First.
Below is the pictorial example of Stack:
Below are the various operations that can be performed on a Stack:
- Push: Insert element to stack
- Pop: Remove element from stack
- Overflow: Check if stack is full
- Under flow: Check if stack is empty.
- Display: Show the contents of the stack.
Below are the important functions that we will be using:
1. push ():
We use push operation to insert an element into the stack. Here before pushing an element into the stack, we should make sure that the stack is having enough space for that operation.
That can be done by checking the present stack size and maximum stack size. If the present stack size is less than maximum stack size, then we will insert the element and increment the present stack size by one.
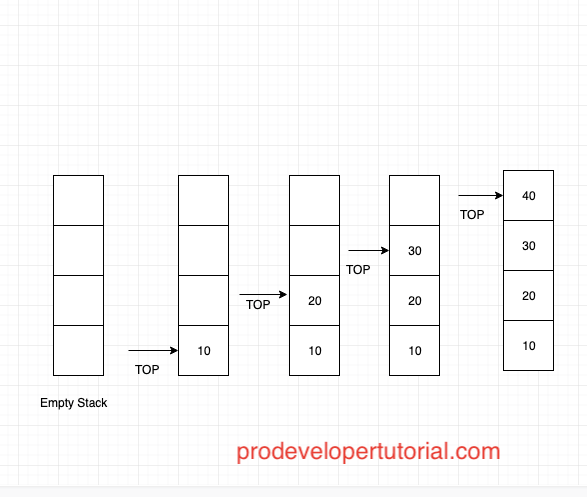
Below is the pictorial example of push operation:
Here we are inserting 10, 20, 30, 40 into the stack.
2. pop ():
We use pop to remove/delete an element from the stack. Before removing an element, we need to check if the stack has some elements.
Removing elements from a stack having no elements will result in Stack Underflow.
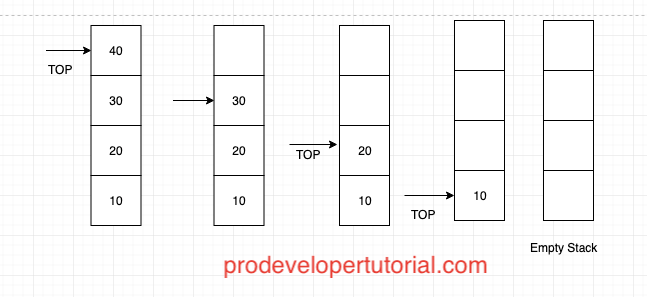
Below is the pictorial example of pop operation:
Here we are removing 40, 30, 20, 10 from the stack.
3. display ()
Display method is used to display all the elements from the stack. If there are no elements, then appropriate error message should be displayed.
Stacks can be implemented in 2 ways.
- Using arrays
- Using Linked List
In this tutorial we shall see how to implement stack using arrays. In the next tutorial we shall see how to implement stacks using linked list.
C program to implement stack using arrays:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define STACK_SIZE 5
int top_index = 0; /* Variable to hold top index */
int stack_items[10]; /* Array to hold stack items */
int item = 0; /* Variable to hold the value to be inserted into stack*/
//function to check if stack is full
int IsFull()
{
return (top_index == STACK_SIZE - 1);
}
//function to insert an element in stack
void push()
{
if (IsFull())
{
printf("Stack is full. Cannot insert more elements \n");
return;
}
top_index = top_index + 1;
stack_items[top_index] = item;
}
//function to check if the stack is empty
int IsEmpty()
{
return top_index == -1;
}
//function to delete an element in stack
int pop ()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
return -1;
}
return stack_items[top_index --];
}
// function to display elements in the stack
void display()
{
if(top_index == -1)
{
printf("Stack is empty\n");
return;
}
printf("The contents of the stack are:\n");
for (int i = 0; i <= top_index; ++i)
{
printf("%d\n", stack_items[i]);
}
return;
}
int main()
{
int deleted_item = 0;
int choice = 0;
top_index = -1;
for( ; ; )
{
printf("1. Push \n2. Pop \n3. Display \n4. Exit\n");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
printf("\nEnter the item to be inserted\n");
scanf("%d", &item);
push();
break;
case 2:
deleted_item = pop();
if(deleted_item == -1)
{
printf("Stack is empty\n");
}
else
{
printf("Deleted Item = %d\n",deleted_item );
}
break;
case 3:
display();
break;
default:
exit(0);
}
}
return 0;
}
Output:
1. Push 2. Pop 3. Display 4. Exit 3 Stack is empty 1. Push 2. Pop 3. Display 4. Exit 1 Enter the item to be inserted 2 1. Push 2. Pop 3. Display 4. Exit 1 Enter the item to be inserted 3 1. Push 2. Pop 3. Display 4. Exit 3 The contents of the stack are: 2 3 1. Push 2. Pop 3. Display 4. Exit 2 Deleted Item = 3 1. Push 2. Pop 3. Display 4. Exit 3 The contents of the stack are: 2 1. Push 2. Pop 3. Display 4. Exit 4