In this chapter we shall study about following topics:
- One Dimensional array
- Characteristics of an array
- Accessing array elements through pointers
- Arrays of pointers
- Passing a single array element to a function
- Passing whole array to a function
- Two dimensional array
An array is a collection of elements of same type. It is a linear and homogeneous data structure. Once the array is created, its size if fixed. You cannot increase or decrease the length of an array.
1. One Dimensional array
Syntax for 1D array:
<data-type> <variable-name> [ size ];
Example:
int arr [20];
Initialization of an array:
int arr[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
2. Characteristics of an array
- Creating an array of 5 integers is equal to creating 5 integer variable.
- Array elements are accessed through index.
- Index for an array starts from 0.
- Total size of the array is equal to size of data-type * number of elements in the array.
Simple example to store the elements in an array and display them.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5];
cout<<"enter 5 numbers"<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) // as we are starting the array from 0.
{
cin>>arr[i];
}
cout<<"The entered elements are"<<endl;
// here the elements are accessed one by one.
cout<<arr[0]<<endl;
cout<<arr[1]<<endl;
cout<<arr[2]<<endl;
cout<<arr[3]<<endl;
cout<<arr[4]<<endl;
}
Output:
enter 5 numbers 5 4 3 2 1 The entered elements are 5 4 3 2 1
3. Accessing array elements through pointers
As arrays are stored in contiguous memory locations, the array elements can be accessed through pointer.
Below is the example for the same:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int *ptr = NULL;
ptr = &arr[0]; // assign the address of first variable of the array to the pointer
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
cout <<" The address of arr["<<i<<"] is = "<< (ptr + i)<<" The value is = "<< *(ptr + i)<<endl;
}
}
Output:
The address of arr[0] is = 0x7ffeebf53ad0 The value is = 1 The address of arr[1] is = 0x7ffeebf53ad4 The value is = 2 The address of arr[2] is = 0x7ffeebf53ad8 The value is = 3 The address of arr[3] is = 0x7ffeebf53adc The value is = 4 The address of arr[4] is = 0x7ffeebf53ae0 The value is = 5
4. Arrays of pointers
Arrays can also store the address of the variables. Then they are called as arrays of pointers.
Example:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int *arr[3];
int num_1 = 10;
int num_2 = 20;
int num_3 = 30;
arr[0] = &num_1;
arr[1] = &num_2;
arr[2] = &num_3;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
cout <<" The address of number ["<<i<<"] is = "<< arr[i] <<" The value is = "<< *arr[i] <<endl;
}
}
Output:
The address of number [0] is = 0x7ffee0782ab8 The value is = 10 The address of number [1] is = 0x7ffee0782ab4 The value is = 20 The address of number [2] is = 0x7ffee0782ab0 The value is = 30
5. Passing a single array element to a function
A single element can be sent to a function with the help of the index of that variable.
Example:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void display(int a);
int main()
{
int arr[3] = {1, 2, 3};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
display(arr[i]);
}
}
void display(int a)
{
cout<<a << endl;
}
Output
1 2 3
6. Passing whole array to a function
A whole array can be passed to a function, by sending the address of first element.
Example:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void display(int arr[] , int length);
int main()
{
int arr[3] = {1, 2, 3};
display(&arr[0], 3);
return 0;
}
void display(int arr[] , int length)
{
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
{
cout<<arr[i] << endl;
}
return;
}
Output:
1 2 3
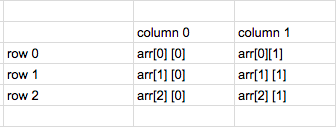
7. Two dimensional array
The visualisation of 3 * 2, 2D array is shown in below image.
Below is the program to show 2D array:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[3] [2] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
for (int row = 0; row < 3; row++)
{
for (int column = 0; column < 2; column++)
{
cout<< " "<< arr[row] [column];
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6